frame
Howdy, Stranger!
It looks like you're new here. If you want to get involved, click one of these buttons!
Sign In RegisterHowdy, Stranger!
It looks like you're new here. If you want to get involved, click one of these buttons!
Quick Links
Categories
- 1.4K All Categories
- 7.3K General
- 6.2K General Discussions
- 412 Feature Request/Bug Report
- 545 Sales Questions and Answers
- 54 Time4VPS Life
- 242 Help requests
- 244 Server management
- 390 Tutorials
- 68 Various Tutorials
- 71 Web hosting control panels
- 133 Performance and Security
- 29 Web Applications
- 64 Linux Applications
- 25 Windows VPS
[CentOS 7/ AlmaLinux 8] How to install MySQL
 Michail
Moderator
Michail
Moderator
Introduction
MySQL is one of the most widely used database management systems on the Internet today. This system is used to work with fairly large volumes of information. However, MySQL is ideal for both small and large Internet projects. Reliability, high speed and flexibility are the main qualities of MySQL.
In this guide we will show you how to install MySQL on RedHat based distributions (CentOS 7, AlmaLinux 8).
WARNING
CentOS 7 reached the EOL June 30, 2024:
https://blog.centos.org/2023/04/end-dates-are-coming-for-centos-stream-8-and-centos-linux-7/
Because of this, you may encounter some repository issues. We recommend that you reinstall another OS that has not yet reached EOL.
If you are using CentOS 7 and encounter a mirror issue, please check out this guide to resolve the problem.
Installation guide
Step for AlmaLinux 8 only: Import GPG key repository
This step is for AlmaLinux 8 only. Skip this step on CentOS 7.
Run the following command to install updated GPG keys on AlmaLinux 8:
rpm --import https://repo.almalinux.org/almalinux/RPM-GPG-KEY-AlmaLinux
1. Updating the system
First of all, make sure your system is updated.
On CentOS 7, run this command:
yum update
On AlmaLinux 8, run the following:
dnf update
2. Download MySQL
To download MySQL setup files, you first need to navigate to MySQL community website:
https://dev.mysql.com/downloads/repo/yum/
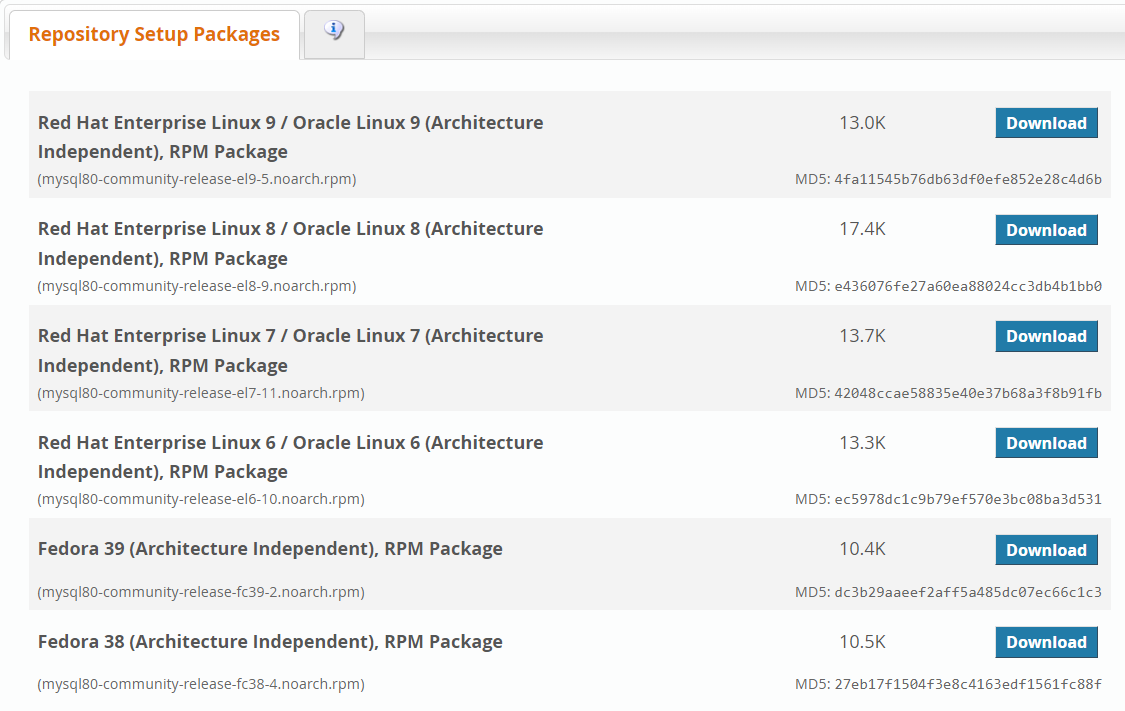
On this page you will see a list of setup packages for different systems. To download packages, copy the gray subtext under the package name. For CentOS 7 select "Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7 / Oracle Linux 7 (Architecture Independent), RPM Package":
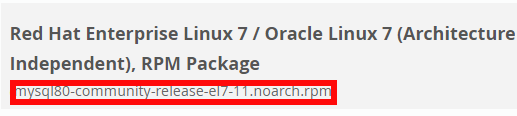
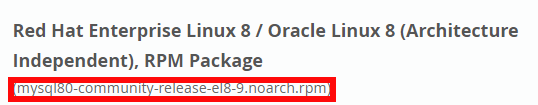
For AlmaLinux 8 select "Red Hat Enterprise Linux 8 / Oracle Linux 8 (Architecture Independent), RPM Package " :
Then type to your terminal the following command:
wget https://dev.mysql.com/get/mysql80-community-release-el7-11.noarch.rpm
In this command, you need to type wget, then the address https://dev.mysql.com/get/ and the package name (in our example, the package for CentOS 7 mysql80-community-release-el7-11.noarch.rpm). Run the command, and it should download the required packages to your server.
3. Checking MySQL repository packages
To check if packages are downloaded correctly, run the md5sum command together with the setup name:
md5sum mysql80-community-release-el7-11.noarch.rpm
The output of this command is a combination of numbers and letters. Compare it with the MD5 value provided in the download link on the MySQL website:
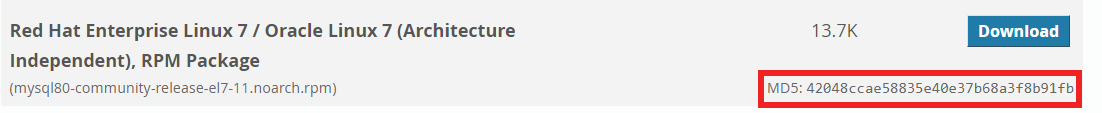
If they match, then the packages were loaded correctly. If not, repeat step 2 and make sure you follow the instructions correctly.
4. Add repositories
To add MySQL yum repositories run the rpm command together with the package name you have downloaded previously:
rpm -ivh mysql80-community-release-el7-11.noarch.rpm
5. Install MySQL
To install MySQL, run the following command:
yum install mysql-server
The system will ask for confirmation, you will need to press Y several times to confirm.
6. Start MySQL
To start MySQL, run the following command:
systemctl start mysqld
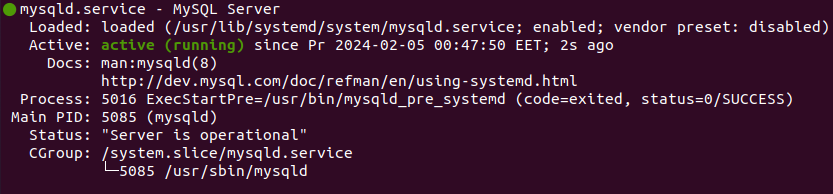
7. Check MySQL status
To check if MySQL is active, run the following command:
systemctl status mysqld
8. Temporary MySQL password
On AlmaLinux 8, skip this step.
To find the default temporary MySQL root password on CentOS 7, run the following command:
grep 'temporary password' /var/log/mysqld.log
In the output, you will get a temporary password that you can save in a safe place.
9. Changing temporary password
Now, to change the temporary password, run the following command:
mysql_secure_installation
On CentOS 7, you will receive this message:
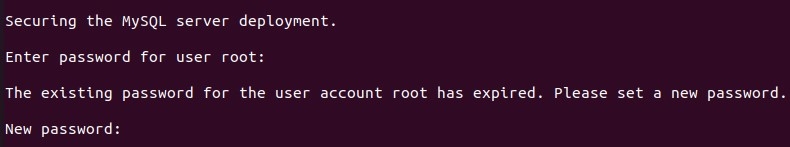
Enter the new password and repeat it. Strong passwords should contain 8-12 characters with letters, numbers and symbols.
After you entered password, press Enter and you will be asked if you want to change your password again. You can enter No for this prompt. For all of the following prompts, you can enter Yes (confirm that other remote users will not be able to connect to the root system and test database and that permissions of unknown users will be removed).
On AlmaLinux 8 you will receive the following message:
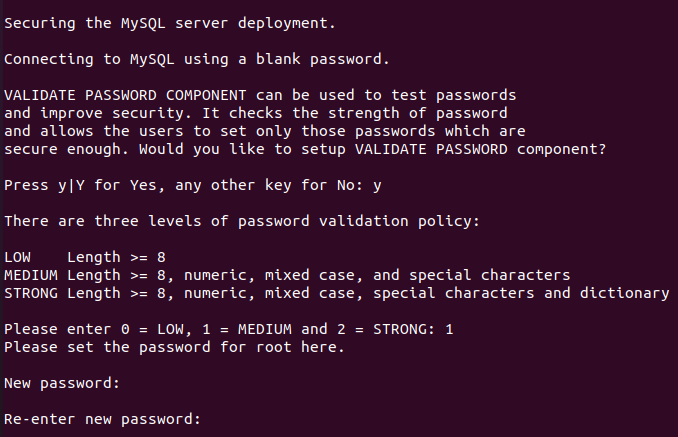
Click "y" to continue. There are three levels of password validation policy on AlmaLinux 8 for MySQL, so you should select the one you want.
To select it, enter the appropriate number and then the password that meets the requirements of the selected policy.
After that, you can enter "y" for all the following requests.
10. Connecting to MySQL server
To connect to MySQL as root, run the following command:
mysql -u root -p
You will asked to enter your root password. Type the password and press enter.
Later, to exit MySQL, enter:
exit
Additional configurations
Create a database
To create a database, connect to MySQL and enter the following command (change "database_name" to the actual database name):
CREATE DATABASE database_name;
Create a user
To create a user, run this command (change the 'username' and 'password' to the actual credentials you want to use):
CREATE USER 'username'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'password';
Delete a user
To delete a user, run the following command (type your actual username instead of 'username' to remove a specific user):
DROP USER ‘username’@‘localhost’;
Reset user password
You can reset your root password or any other user password at any time. To do that, connect to MySQL as root and run the following command:
ALTER USER 'your_user'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED WITH mysql_native_password BY 'new_password';
Disable or stop the MySQL service
MySQL is loaded at system boot by default, however you can disable it manually at any time:
systemctl disable mysqld
To stop the MySQL service, run the following command:
systemctl stop mysqld


