frame
Howdy, Stranger!
It looks like you're new here. If you want to get involved, click one of these buttons!
Sign In RegisterHowdy, Stranger!
It looks like you're new here. If you want to get involved, click one of these buttons!
Quick Links
Categories
- 1.4K All Categories
- 7.3K General
- 6.2K General Discussions
- 412 Feature Request/Bug Report
- 545 Sales Questions and Answers
- 54 Time4VPS Life
- 242 Help requests
- 244 Server management
- 390 Tutorials
- 68 Various Tutorials
- 71 Web hosting control panels
- 133 Performance and Security
- 29 Web Applications
- 64 Linux Applications
- 25 Windows VPS
How To Install Apache web server on CentOS 7/AlmaLinux 8/AlmaLinux 9
 Michail
Moderator
Michail
Moderator
Introduction
The Apache HTTP web server is currently the most popular web server software in the world. It is well suited for working with large projects and is very flexible in terms of configuration, which makes it possible to implement all the features of the hosted web resource.
In this guide you will learn how to install Apache web server on RedHat based distributions (CentOS, AlmaLinux).
WARNING
CentOS 7 reached the EOL June 30, 2024:
https://blog.centos.org/2023/04/end-dates-are-coming-for-centos-stream-8-and-centos-linux-7/
Because of this, you may encounter some repository issues. We recommend that you reinstall another OS that has not yet reached EOL.
If you are using CentOS 7 and encounter a mirror issue, please check out this guide to resolve the problem.
Step for AlmaLinux 8 only: Import GPG key repository
This step is for AlmaLinux 8 only. Skip this step if you are installing Apache on CentOS 7 or AlmaLinux 9.
Run the following command to install updated GPG keys on AlmaLinux 8:
rpm --import https://repo.almalinux.org/almalinux/RPM-GPG-KEY-AlmaLinux
1. Installing Apache
Make sure your software is updated before the actual installation. You can do this with the following command:
yum update
After updating the packages, run the following command to install Apache:
yum install httpd
2. Starting Apache
To start Apache, run this command:
systemctl start httpd
3. Apache status check
To check Apache status, run the following command:
systemctl status httpd
The output will provide Apache and some additional information:
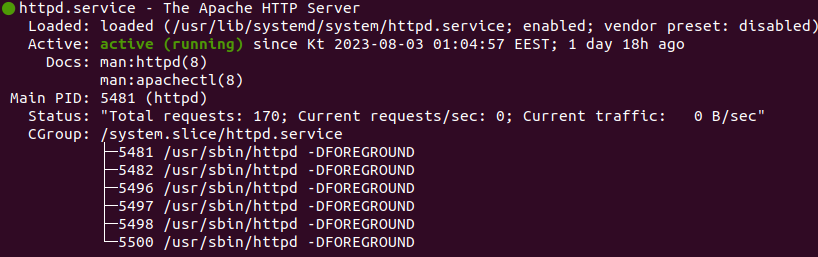
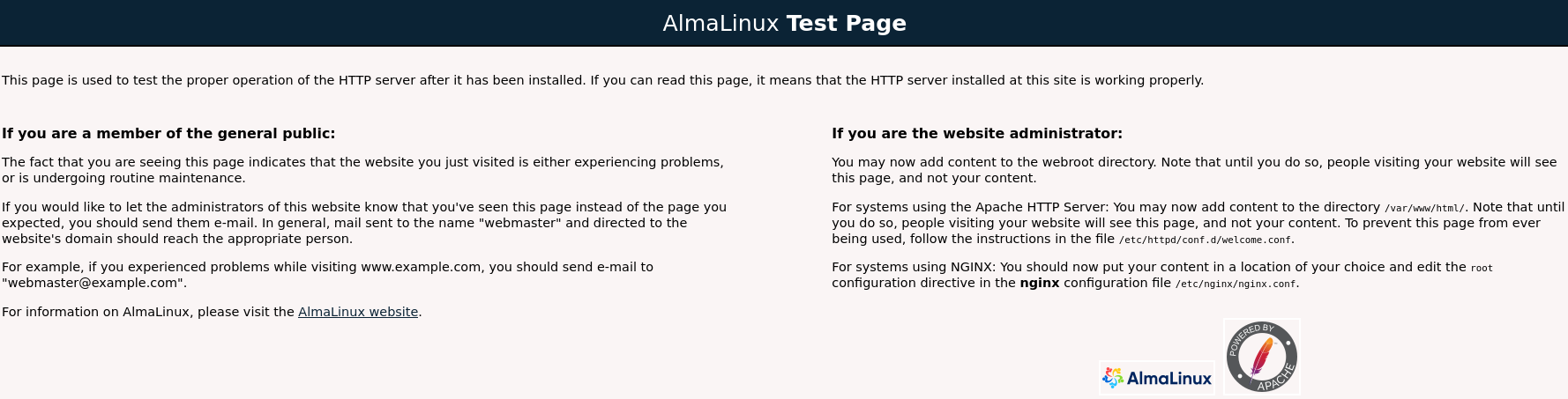
You can also verify if Apache was enabled on your server, by entering your server's public IP address in your web browser:
If everything is correct, you will see the default Apache web page (different for CentOS and AlmaLinux):
CentOS:

AlmaLinux:
4. Additional configurations
If you don't want Apache to start automatically on every system boot, run the following command:
systemctl disable httpd
If you want to re-enable this feature and automatically start Apache after every boot, run the following command:
systemctl enable httpd
To stop Apache, run this command:
systemctl stop httpd
You can restart Apache with:
systemctl restart httpd
To reload Apache without losing connections, enter the following command:
systemctl reload httpd
5. Virtual Host (optional)
VirtualHost is a directive in the configuration file of the Apache web server, designed to match IP addresses available on the server, domains and directories on the server, as well as manage sites available on the server.
You can create a virtual host configuration file by typing this command:
vi /etc/httpd/conf.d/yourdomain.ltd.conf
Add these lines to the configuration file:
<VirtualHost *:80> ServerAdmin [email protected] DocumentRoot "/var/www/html" DirectoryIndex index.html ServerName yourdomain.ltd ErrorLog "/var/log/httpd/yourdomain.ltd.error_log" CustomLog "/var/log/httpd/yourdomain.ltd.access_log" common </VirtualHost>
After editing, you can save changes and exit.
Be sure to restart Apache after creating the configuration file:
systemctl restart httpd
To establish a secure connection, you can check our guide for Let's Encrypt.


